In a significant new development in the Faketoshi saga, the European Patent Office (EPO) has revoked European patent EP3449450, held by nChain Licensing AG. This decision comes after an opposition filed by Arthur van Pelt in October 2022. The patent, which pertains to blockchain technology, is the first from nChain to be revoked. The oral proceedings scheduled for 2 July 2024 were cancelled as the patent proprietor requested the revocation.
Details of the Revocation
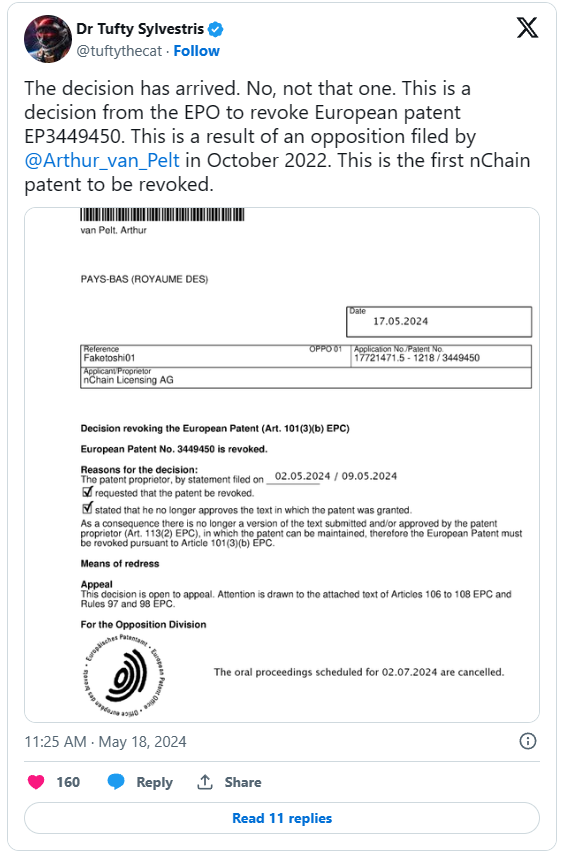
The EPO’s decision was based on the patent proprietor’s statement filed on 2 May and 9 May 2024, requesting the patent’s revocation. This statement also indicated that the proprietor no longer approves the text in which the patent was granted. As there is no longer an approved version of the text for the patent, it must be revoked under Article 101(3)(b) EPC.
David Pearce (aka Dr. Tufty Sylvestris), a patent attorney highlighted this development in a tweet, underscoring the impact of the revocation and providing updates on the continuing proceedings for related patents. Pearce has been actively involved in the cases of these patents and the ongoing opposition efforts.
Fun fact: The official reference names of the opposition documents are Faketoshi01, Faketoshi02, Faketoshi03 etc.
Editor
Background and Opposition
Arthur van Pelt, a known critic of Craig Wright and nChain, filed the opposition that led to this revocation. In his earlier communications, van Pelt expressed skepticism about the patent’s chances of surviving the opposition, a prediction that has now been validated. The decision marks a crucial victory for those opposing what they view as overreaching patents in the blockchain space.
To provide some context in terms of available comparable statistics, the opposition rate varies by technology field. According to the European Patent Office (EPO), the overall opposition rate is around 2.5% across all technology fields. However, certain fields such as biotechnology and pharmaceuticals have higher opposition rates, at 5.3% and 5.7% respectively. The EPO processes thousands of oppositions each year, with a significant number leading to partial or full revocation of the patents in question.
Future Implications and Ongoing Proceedings
While this decision concludes the journey for EP3449450, it is not the end for nChain’s patent family. There are two additional patents in the same family that have also faced opposition, with proceedings still ongoing. Additionally, there are three more pending oppositions related to these patents.


Community Support and Contributions
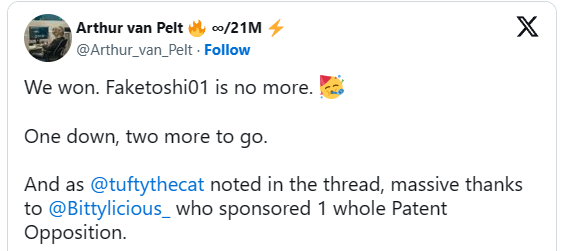
In his tweet, David Pearce expressed gratitude to all contributors who helped cover the official fees for the opposition of nChain’s European patents. A special acknowledgment was given to Bittylicious, a cryptocurrency exchange, for fully covering the opposition fee for one of the patents. This collaboration highlights the community’s significant role in challenging patents that could stifle innovation in the blockchain space.
Bittylicious responded to Pearce, appreciating the hard work put into the opposition and expressing satisfaction in seeing the positive outcome. The exchange’s contribution was crucial in facilitating the opposition process, demonstrating the power of collective effort in achieving significant legal victories.
Pearce reflected on the experience, describing it as both interesting and enjoyable. This story shows that community engagement and support in legal battles, is crucial, especially in complex fields like intellectual property and blockchain technology.
Why is a Patent Revoked?
Patents can be revoked for a variety of reasons, typically related to issues of patentability, procedural errors, or the actions of the patent holder. Here are some common reasons why patents get revoked:
Lack of Novelty and Inventive Step: Novelty: A patent may be revoked if it is found that the invention was not new at the time the patent application was filed. If the invention had already been disclosed to the public, either through prior patents, publications, or public use, it fails the novelty requirement. Inventive Step: Even if an invention is new, it must also be non-obvious to someone skilled in the field. If it is determined that the invention is an obvious improvement or combination of existing technologies, the patent can be revoked.
Insufficient Disclosure: A patent must fully disclose the invention in a manner that allows others skilled in the art to reproduce it. If the patent application fails to provide enough detail or contains misleading information, it can be revoked for insufficient disclosure.
Unpatentable Subject Matter: Certain inventions may not be eligible for patents based on their subject matter. For instance, abstract ideas, natural phenomena, and mathematical formulas are generally not patentable. If a patent is granted for such unpatentable subject matter, it can be revoked.
Procedural Errors: Errors in the application process, such as failing to meet filing deadlines, paying required fees, or providing necessary documentation, can lead to the revocation of a patent. Compliance with procedural requirements is crucial for maintaining a patent’s validity.
Opposition and Third-Party Challenges: Patents can be challenged by third parties through opposition proceedings. These challenges often occur soon after a patent is granted and can lead to revocation if the opposition proves that the patent does not meet the necessary legal requirements.
Patent Holder’s Request*: In some cases, the patent holder may request the revocation of their own patent. This can happen for various strategic reasons, such as avoiding legal disputes or maintaining focus on other patents.
Case Study: Revocation of nChain Patent EP3449450
The revocation of European patent EP3449450 held by nChain Licensing AG is an example of revocation due to the patent holder’s request. Arthur van Pelt filed an opposition against the patent, and the patent proprietor eventually requested its revocation, stating they no longer approve the text in which the patent was granted. This led to the EPO revoking the patent under Article 101(3)(b) EPC.
Reactions
Arthur van Pelt, who played a pivotal role in this opposition, expressed his satisfaction and relief following the EPO’s decision. In a series of tweets, van Pelt highlighted the collaborative effort involved in the opposition process and the support received from the community. His comments shed light on the broader implications of this victory and the challenges faced along the way.
- Community Effort: Van Pelt acknowledged the significant contributions from individuals and organizations, specifically thanking Bittylicious for sponsoring one of the opposition fees. This collective effort underscores the importance of community support in challenging potentially overreaching patents that could stifle innovation.
- Challenges and Triumphs: Reflecting on the journey, van Pelt noted the various hurdles overcome to reach this point. He compared the situation to other notable cases in the blockchain and cryptocurrency space, highlighting the resilience required to contest such patents successfully.
- Future Proceedings: While celebrating this victory, van Pelt also pointed out that this is just the beginning. There are still two more patents in the same family facing opposition, with proceedings ongoing, and three additional pending applications. The community remains vigilant and prepared to continue the fight to ensure that the fallout of the Faketoshi saga does not continue.
The revocation of EP3449450 by the EPO signifies a key moment in the ongoing scrutiny of blockchain-related patents. This outcome not only reflects the robustness of the opposition process but also highlights the community’s role in challenging patents that they believe may hinder innovation.
As proceedings for other related patents continue, this case is far from over. According to previous information provided by Pearce this has been one of the busiest years for nChain patent filings and many more might be challenged in courts.
Author Profile

- Lucy Walker covers finance, health and beauty since 2014. She has been writing for various online publications.
Latest entries
- June 30, 2025NewsWireBank Savings at Risk: The Dark Side of EU’s Savings Standard
- April 25, 2025Global EconomicsWhistleblowers Unmask Schwab’s Toxic WEF Secrets
- April 9, 2025Global EconomicsTariff Tensions Drive Market Volatility
- March 18, 2025Global EconomicsRed in Name Only: Labour’s War on the UK Working Class