For decades, economists and policymakers have warned of the destructive effects of inflation says Graham Cooke, an ex-Google executive and CEO of financial systems company Brava. He says that they are pointing to rising prices as a central threat to economic stability. But what many fail to account for is a larger, transformative force at work: technology. As artificial intelligence (AI) merges with robotics, 3D printing, and renewable energy, the costs of production across industries are poised to plummet, ushering in an era of abundance that could reshape our global economy. This deflationary force, though less discussed, may hold the key to navigating the challenges of the modern economic landscape, claims Cooke.
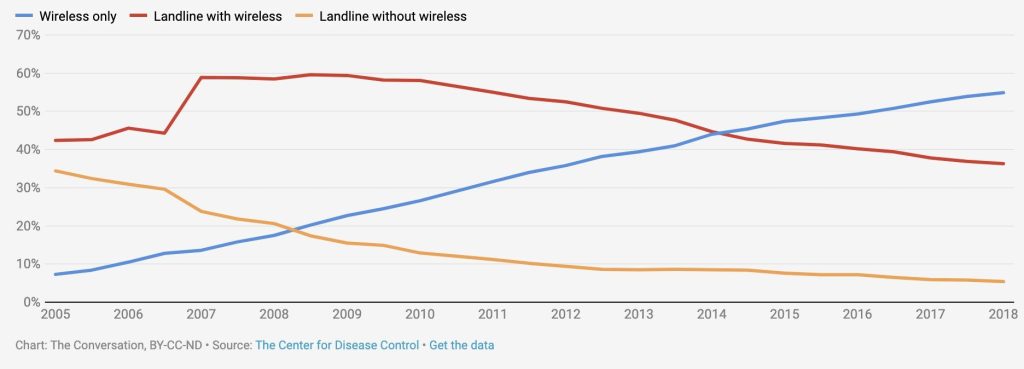
To understand the scale of what’s happening, consider the dramatic decline in communication costs over the past century. In 1934, a simple 3-minute phone call cost the equivalent of $700 in today’s money. This was due to the expensive infrastructure required: copper wiring across continents, manual operators, and limited bandwidth. Communication was a luxury, reserved for those who could afford it.
Then came a wave of technological breakthroughs. Fiber optic cables replaced copper wiring, digital switching eliminated the need for manual operators, and satellites extended communication’s reach globally. Each innovation slashed expenses dramatically. By the early 2000s, that same call cost just $5. By 2010, less than $1. Today, apps like WhatsApp and Zoom make global communication effectively free.
This isn’t an isolated story. Similar patterns of cost reduction have played out in storage, energy, and countless other sectors. For example, the cost of storing one gigabyte of data has fallen from $1 million in 1980 to just $0.02 today. This is the superpower of technology: it doesn’t just reduce costs—it transforms industries.
The Role of AI in Accelerating Deflation
Artificial intelligence represents the next phase in this deflationary cycle, one that promises to surpass anything we’ve seen before. AI doesn’t just optimize processes. It fundamentally changes how products are designed, manufactured, and delivered. By combining AI with complementary technologies like robotics and 3D printing, production becomes faster, cheaper, and more efficient.
Take manufacturing as an example. AI-powered robots can work around the clock without fatigue, reducing labor costs and errors. 3D printing enables the creation of complex products on demand, eliminating waste and minimizing supply chain delays. When renewable energy is added to the mix, energy costs, a major factor in production, become negligible. Together, these forces create a feedback loop:
- Supply increases dramatically
- Costs drop significantly
- Prices fall for consumers
This deflationary cycle doesn’t just make existing products cheaper; it enables the creation of entirely new categories of goods and services that were previously impossible. Smartphones didn’t just replace landlines, they unlocked entirely new industries, from app development to mobile gaming. AI will do the same, with applications we can barely imagine today.
While governments continue to print money at unprecedented rates, leading to inflation, technology counters this with its deflationary power. This creates a fascinating economic paradox: on one hand, monetary policies erode the value of money; on the other, technology continually increases the value of what money can buy.
Consider this: today, services that once cost thousands of dollars are available for free. Global video calls, infinite cloud storage, world-class education, and professional-grade software, all are accessible at little to no cost. This isn’t just a matter of convenience; it’s a shift in the very foundations of our economic system.
When costs approach zero, traditional business models are upended. Companies must find new ways to generate revenue, often by offering value-added services or monetizing data. This shift opens the door to what some call an “era of abundance,” where the essentials of life (communication, education, energy) are accessible to all.
The impact of this technological revolution is staggering when compared to historical benchmarks. Goldman Sachs estimates that AI could boost global labor productivity by 0.3% to 3.0% annually over the next decade. For context, the Industrial Revolution, often hailed as the most transformative economic shift in history, increased productivity by just 0.8% annually.
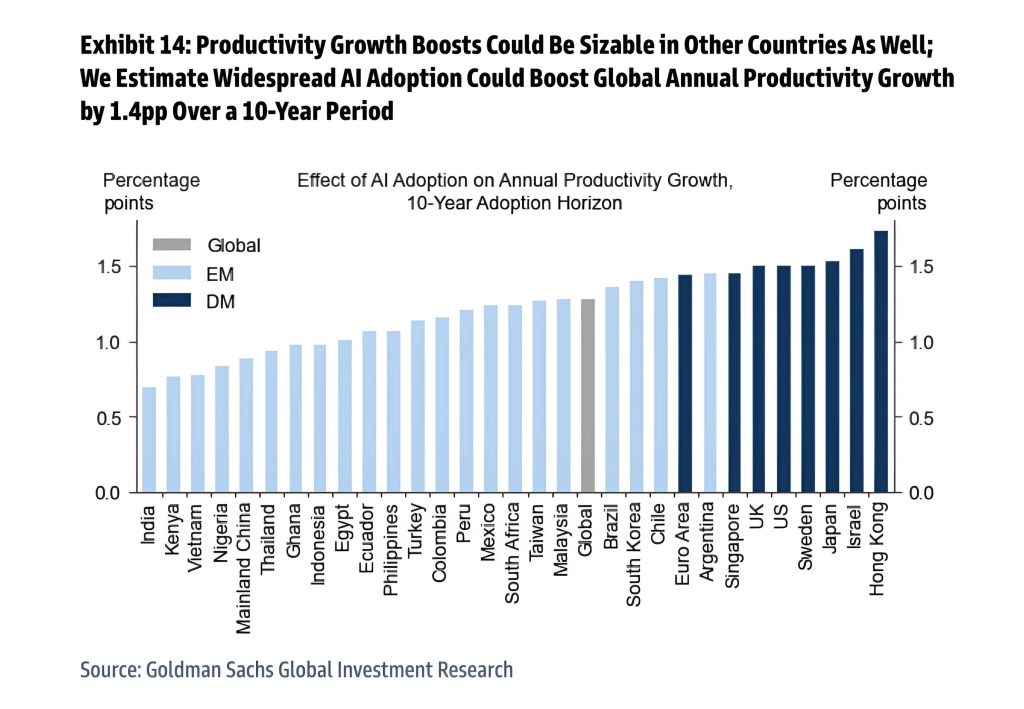
This rapid acceleration means the economic impact of AI, combined with complementary technologies, will be felt much faster than previous technological shifts. As these innovations scale, industries will be reshaped, new markets will emerge, and the very structure of global economies will evolve.
The deflationary power of technology brings immense opportunities, but it also poses challenges. While consumers benefit from lower prices and greater access, traditional industries may struggle to adapt. Governments, too, face a dilemma: how to balance inflationary monetary policies with the deflationary forces of technology.
Yet, the evidence is clear. Technology is the most powerful deflationary force in history, and it’s just getting started. As AI, robotics, 3D printing, and renewable energy continue to advance, the cost of production across industries will approach zero, paving the way for a new economic paradigm.
A New Economic Era
As we navigate an uncertain economic future, one thing is clear: technology, not monetary policy, will define the trajectory of global economies. The fusion of AI, robotics, and renewable energy represents a once-in-a-century transformation, one that will shape how we live, work, and interact for decades to come. While inflation remains a concern, the deflationary power of technology offers hope for a future where abundance, rather than scarcity, becomes the norm.
Graham Cooke (GC Cooke) is the CEO and Founder of Brava, a company at the forefront of revolutionizing financial systems through blockchain and AI. With a career that spans major industry players like Google and ITV, Graham has also founded and exited successful ventures such as Qubit. He is the author of “Web3: The End of Business as Usual”, where he explores how decentralized technologies are reshaping industries. Known for his thought leadership in emerging tech and economics, Graham continues to advocate for smarter, more efficient financial ecosystems.
Author Profile

- Lucy Walker covers finance, health and beauty since 2014. She has been writing for various online publications.
Latest entries
- June 30, 2025NewsWireBank Savings at Risk: The Dark Side of EU’s Savings Standard
- April 25, 2025Global EconomicsWhistleblowers Unmask Schwab’s Toxic WEF Secrets
- April 9, 2025Global EconomicsTariff Tensions Drive Market Volatility
- March 18, 2025Global EconomicsRed in Name Only: Labour’s War on the UK Working Class